- Print this page
- Download as PDF
- Share this page
Most foodborne illness is caused by pathogenic bacteria or viruses in food.
Other less common foodborne illness occurs from accidental chemical poisoning and natural contaminants.
The most common types of foodborne illness are:
- bacterial eg Salmonella, Campylobacter, E.coli and Listeria
- viral eg Norovirus, Rotavirus and Hepatitis A
- intoxication caused by toxins produced by pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus and Clostridium perfringens.
Symptoms and the most frequent food vehicle will vary depending on the type of pathogen.
(Wide table: scroll/swipe sideways if not all columns are displayed.)
| Pathogen | Microscopic image of pathogen ** | Typical incubation period (time between eating and onset of symptoms) | Typical symptoms | Typical food vehicles * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus cereus toxin (vomiting and diarrhoea) |  | 1 - 6 hours 6 - 24 hours | Sudden onset of severe nausea and vomiting Abdominal cramps, nausea and watery diarrhoea | Improperly refrigerated cooked rice and pasta, and fresh noodles Meats, stews, gravy |
| 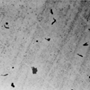 | 2 - 5 days | Fever, nausea, abdominal cramps and diarrhoea (sometimes bloody) | Raw and undercooked poultry, unpasteurised milk and contaminated water |
Clostridium perfringens toxin
| 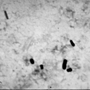 | 6 - 24 hours | Abdominal cramps, watery diarrhoea and nausea | Meats, poultry, gravy, dried or precooked foods |
Escherichia coli including (STEC)
|  | 2 - 10 days more commonly 3 - 4 days | Diarrhoea (often bloody), abdominal cramps | Improperly cooked beef, unpasteurised milk and juice, sprouts and contaminated water |
| 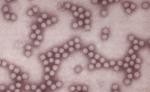 | 2 - 7 weeks | Jaundice, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea | Raw or poorly cooked seafood harvested from contaminated waters, ready-to-eat foods handled by an infected food handler |
| 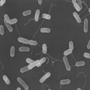 | 3 days - 10 weeks | Meningitis, sepsis, fever | Soft cheeses, unpasteurised milk, ready-to-eat deli meats |
| 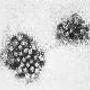 | 24 - 48 hours | Fever, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhoea and headache | Poorly cooked shellfish, ready-to-eat foods touched by an infected worker |
| 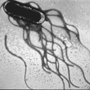 | 6 – 72 hours, usually 12-36 hours | Headache, fever, abdominal cramps, diarrhoea, vomiting and nausea | Undercooked poultry, raw egg desserts and mayonnaise, sprouts, tahini |
Staphylococcus aureus toxin
| 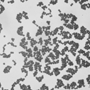 | 0.5 – 8 hours | Sudden onset of vomiting and abdominal cramps | Cream desserts and pastries, potato salad |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
| 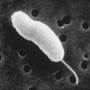 | 4–30 hours, usually 12-24 hours | Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps and watery diarrhoea | Undercooked or raw seafood. |
*The foods shown in the table have previously been found to be the source of the pathogens listed. This does not mean that these foods are always unsafe to eat that such pathogens are always present, or that only these foods can carry the pathogen.
**Image credits: Partnership for Food Safety Education (USA); Laboratory of Clinical and Epidemiological Virology, Catholic University of Leuven (Belgium); HealthNJ, Univesity of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey (USA).
